Electricity
Conductors and insulators - CCEA
Electric current is caused by moving electric charges. The effects of charge and electric fields can be investigated by looking at the forces they exert on conductors and insulators.

Charge, current and voltage - CCEA
Electrical current transfers energy around circuits. There are two types of current: direct and alternating.
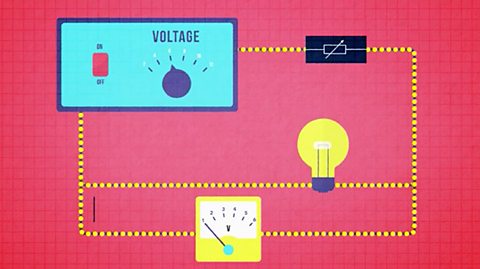
Ohm鈥檚 law, electric power and energy - CCEA
Ohm鈥檚 Law states that the voltage across a conductor is directly proportional to the current flowing through it, provided all physical conditions, such as temperature, remain constant.

Calculating resistance - CCEA
Learn how to calculate resistance in series and parallel circuits, and how resistance depends on length of conductor.

Electricity in the home - CCEA
Electricity can flow either as direct or alternating current, and is used in homes to power electrical appliances.

Links
- External linkExternal link
- External linkExternal link
- External linkExternal link
- External linkExternal link
- SubscriptionSubscription
- External linkExternal link
- SubscriptionSubscription
- External linkExternal link