M2: Geometry and measures
Module 2 (M2) - Geometry & measures - Pythagoras
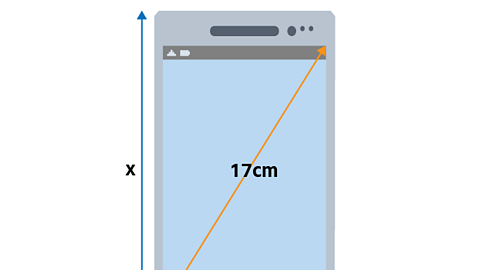
Pythagoras’ Theorem states that, in a right-angled triangle, the square of the longest side is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides.
Module 2 (M2) - Geometry and Measures - Compound measures
Compound measures involve two or more different units. Examples of compound measures and their units include density, speed, heart rate), and miles per gallon.

Module 2 (M2) - Geometry & measures - Compound shapes
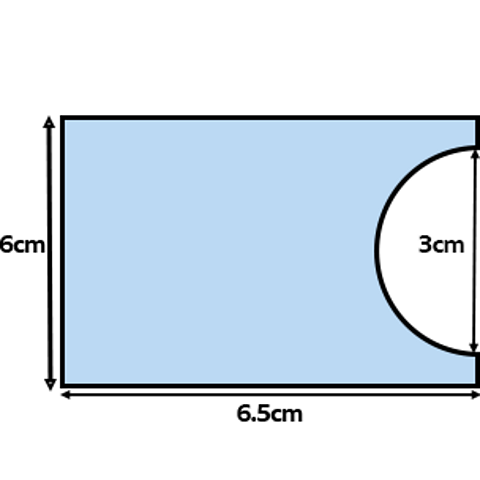
Compound or composite shapes can be made up of two or more shapes or from a shape with a smaller piece removed.
Module 2 (M2) - Geometry & measures - Area
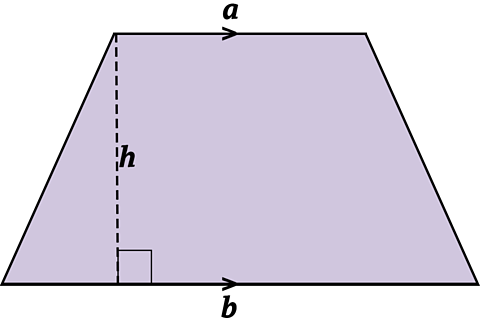
Area is the amount of space taken up by a surface or 2-D shape. It is measured in squares with metric units mm², cm², m² and km².
Links
- External linkExternal link
- SubscriptionSubscription
- External linkExternal link
- External linkExternal link
- External linkExternal link